The Visual Guide to
Bovine Reproduction
- Uterine Torsion
- Strangulated Umbilical Cord
- Pelvic Subluxation
- Prolapsed Vagina
- Prolapse of the Bladder
- Ruptured Prepubic Tendon
- Prolonged Gestation
- Hydrops Allantois
- Hydrops Amnii
- Mummification
- Maceration
Accidents of Gestation: Uterine Torsion
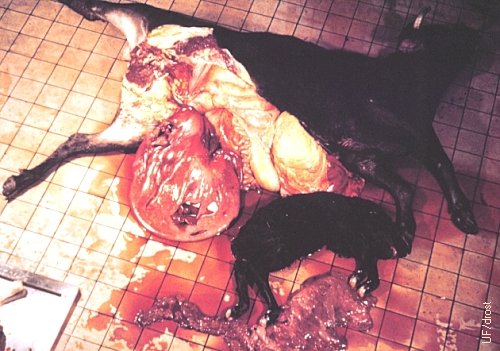
Uterine Torsion with Rupture.
Uterine torsion at term. Severe vascular compromise rendered the uterine wall congested and fragile, and the fetus dropped through the uterine wall.
Roberts SJ (1973)
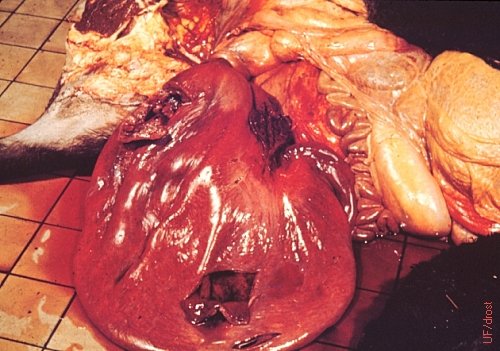
Uterine Torsion - Close Up.
Uterine torsion. Severe vascular compromise rendered the uterine wall congested and fragile.
Roberts SJ (1973)
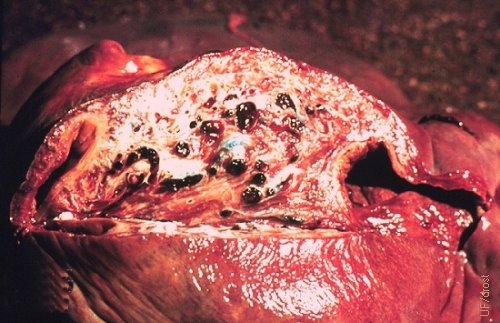
Severe Vascular Congestion of the Uterus.
Uterine torsion at term. Severe vascular compromise rendered the uterine wall congested and thickened. Note cross sections of dilated vessels at the cut surface of the uterine wall.
Roberts SJ (1973)
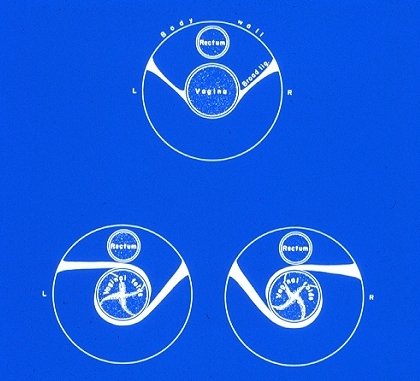
Diagnosis of Uterine Torsion.
The relative position of the broad ligaments is diagrammed for a 180 degree right (clock-wise) uterine torsion (lower left) and a 180 degree left (counter-clock-wise) uterine torsion (lower right).
Roberts SJ (1986)
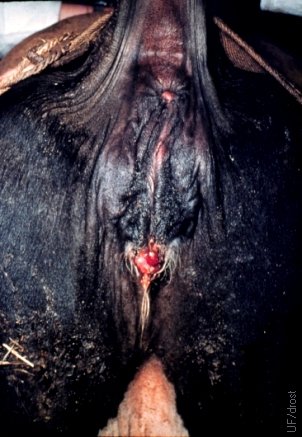
Vulvar Twist.
Subtle twisting of the vulva due to right uterine torsion.
Utrecht (1976)
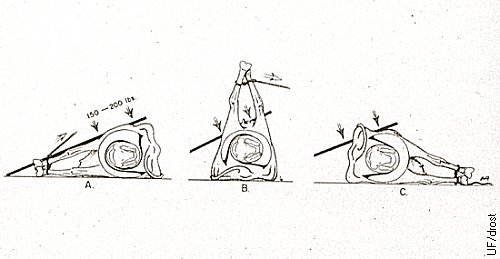
Plank in the Flank Correction.
"Plank in the flank" or Schaffer method of correction of torsion of the uterus by rolling the cow around the fetus which is kept in place by applying pressure to her abdomen by a person standing on a plank. Note the head of the fetus in the diagrams, it does not change position. The cow is rolled around the fetus to correct the torsion.
Roberts SJ (1986)

Correction of Uterine Torsion 1.
Supplies and instruments needed are soap and water, 1.5 m long obstetrical chain, Frick speculum, 1.0 m string, 30 cm cross bar.
Hinson L (2007)
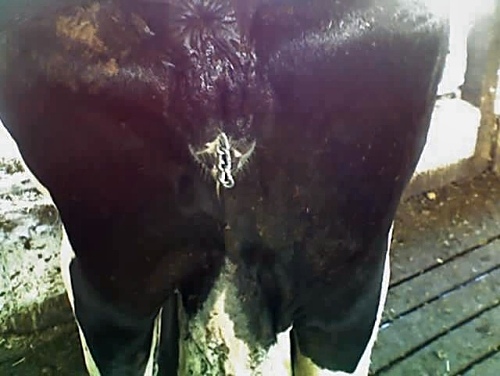
Correction of Uterine Torsion 2.
After the torsion of the uterus has been confirmed, one end of the OB chain is placed on one foot, and the other end of the OB chain on the opposite foot. A small loop of the center of the chain is left hanging out of the vulva.
Hinson L (2007)

Correction of Uterine Torsion 3.
A piece of string or twine is tied to the short piece of the exposed chain.
Hinson L (2007)
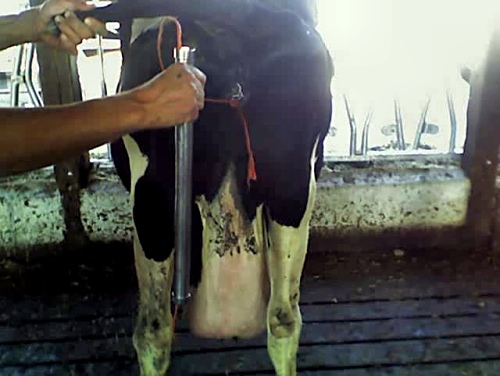
Correction of Uterine Torsion 4.
The string is passed through the speculum.
Hinson L (2007)

Correction of Uterine Torsion 5.
A cross bar is inserted through the small loop of chain that now extends beyond the end of the speculum. This picture illustrates the use of a small dehorner as a cross bar.
Hinson L (2007)

Correction of Uterine Torsion 6.
The cross bar is turned in the proper direction to correct the torsion. The area of the chain between the feet of the calf and the proximal end of the speculum should be checked for entrapment of uterine tissue.
Hinson L (2007)

Correction of Uterine Torsion 7.
When the chain is tight, the calf will turn and correct the torsion of the uterus. The chain should be checked initially for trapped uterine tissue.
Hinson L (2007)
