The Visual Guide to
Bovine Reproduction
Reproductive Technology: In Vitro Fertilization
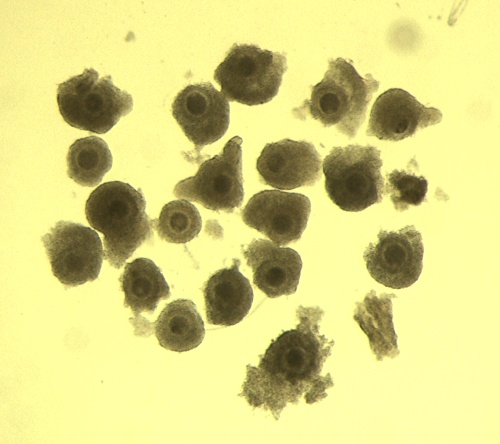
High Quality COC.
These oocytes have several intact layers of cumulus cells. They were isolated by the process of slashing of slaughterhouse ovaries. (Cumulus Oocyte Complex = COC)
Block J (2007)
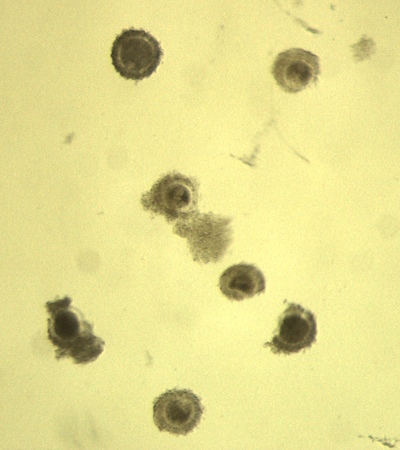
Low Quality COC.
The number of layers is less than three. These COC can still be used, but the rate of development may be lower. (Cumulus Oocyte Complex = COC)
Block J (2007)
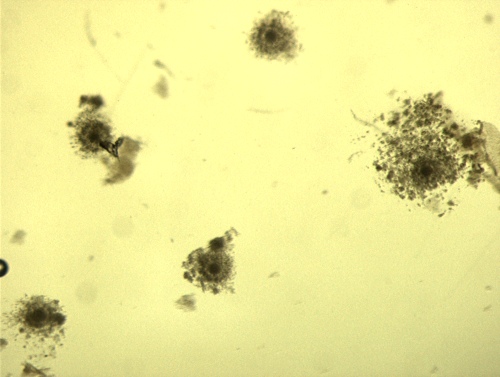
Poor Qualtiy COC.
Oocytes right after harvesting. The cumulus cells had already expanded. These would be excluded from the process of in-vitro fertilization (IVF). (Cumulus Oocyte Complex = COC)
Block J (2007)
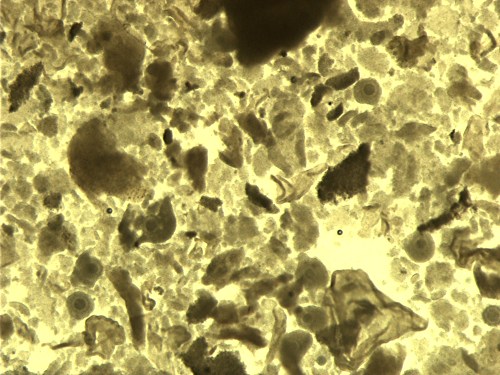
Right After Slashing.
Debris shown right after slashing. Oocytes can be identified at 10 to 25 X, aspirated, washed and transfered to the maturation medium.
Block J (2007)
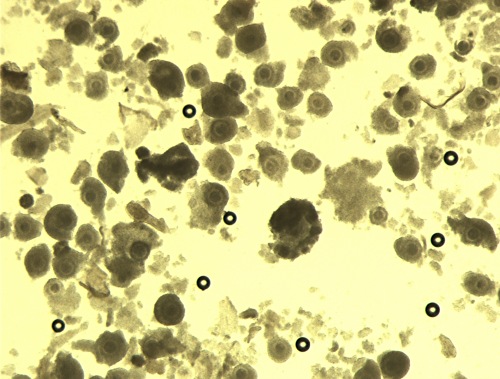
Prior Washing.
Oocytes were removed from the search plate after slashing and are now ready for washing to remove the remaining smaller debris.
Block J (2007)
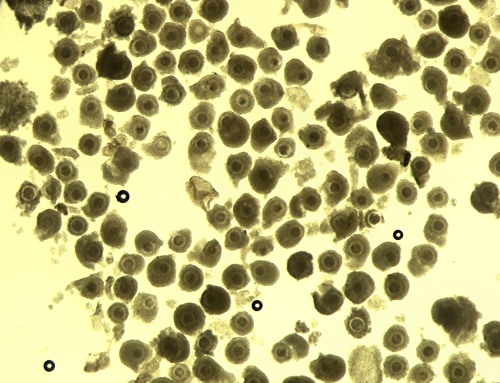
After the Final Wash.
Oocytes after the third and final wash. They are now ready to be placed into the maturation medium.
Block J (2007)
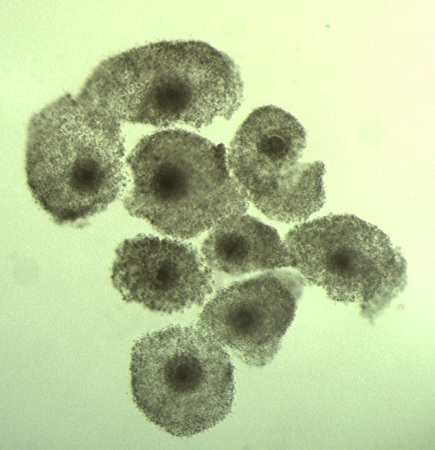
Mature Oocytes.
Very nice mature oocytes with several layers of cumulus cells and homogeneous appearance of the cytoplasm (after 22 to 24 hours of incubation).
Block J (2007)
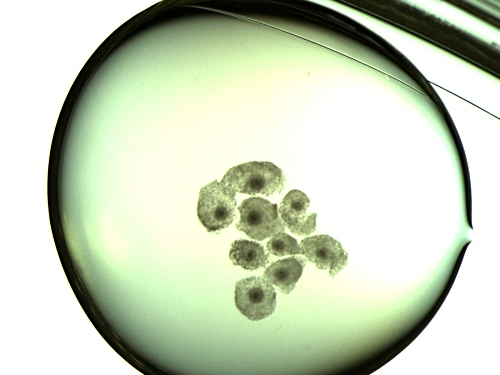
Mature Oocytes in Drop.
Mature oocytes after 22 to 24 hours of incubation shown in a microdrop of maturation medium.
Block J (2007)
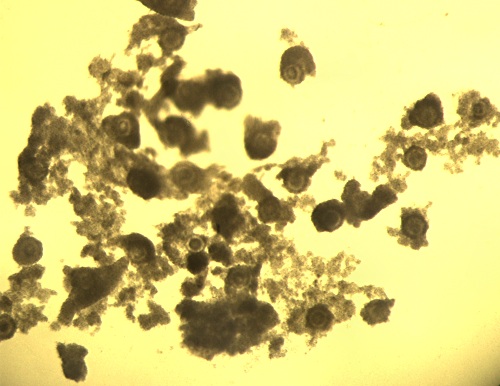
Oocytes After Fertilization.
Oocytes after eight hours of co-incubation with spermatozoa. Cumulus cells have begun to separate from the oocyte proper. The next step is vortexing to remove the attached cumulus cells.
Block J (2007)
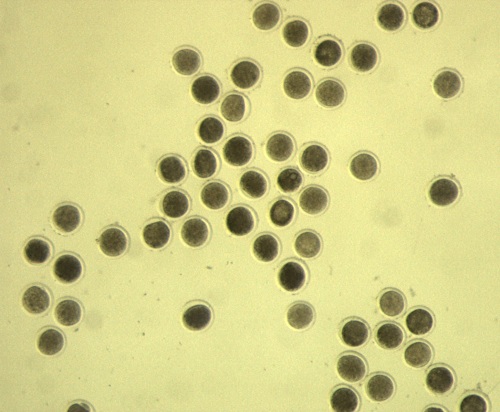
Fertilized Oocytes.
Oocytes eight hours after insemination / exposure to sperm. Cumulus cells were removed by vortexing for 3 to 5 minutes at high speed.
Block J (2007)
