The Visual Guide to
Ovine Reproduction
Male Reproductive System: Vasectomy
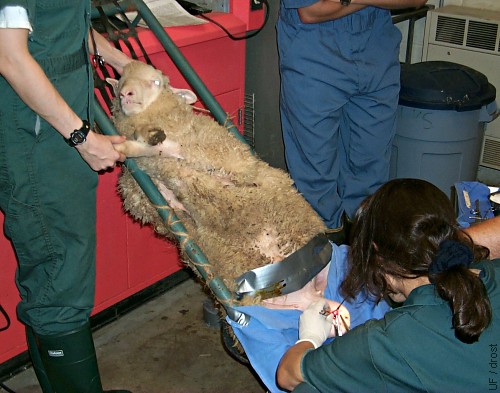
Restraint for Vasectomy.
The ram is restrained in a reclining cradle for a vasectomy.
Smith MC (2006)
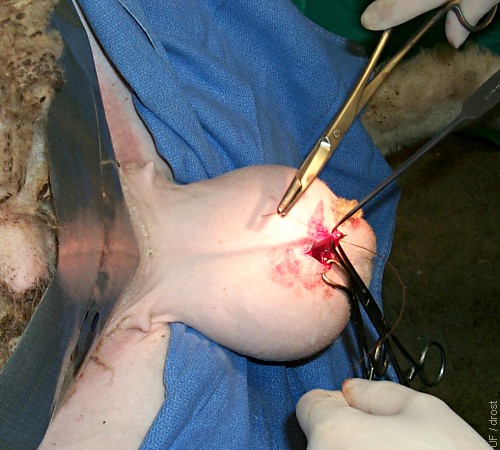
Double Ligation.
Midscrotal approach for vasectomy. The vas deferens is exteriorized and ligated twice and a piece will be removed. The tail of the epididymis was left intact.
Smith MC (2006)
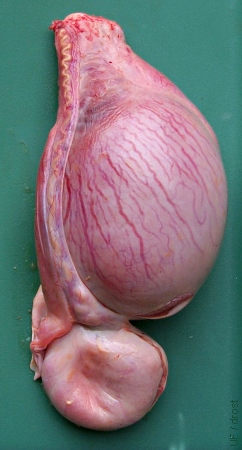
Distended Cauda Epididymidis.
A previous vasectomy by ligation of the vas deferens above the testis has caused accumulation of semen or pus in the tail of the epididymis.
Smith MC (2006)
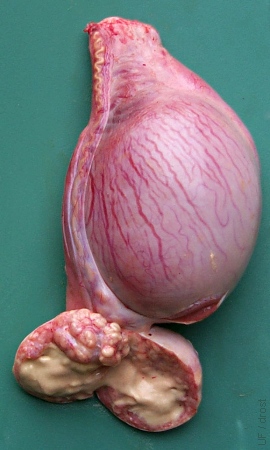
Distended Cauda after Vasectomy.
Previous vasectomy above the testis has resulted in accumulation of sperm and possibly infection of the tail of the epididymis.
Smith MC (2006)
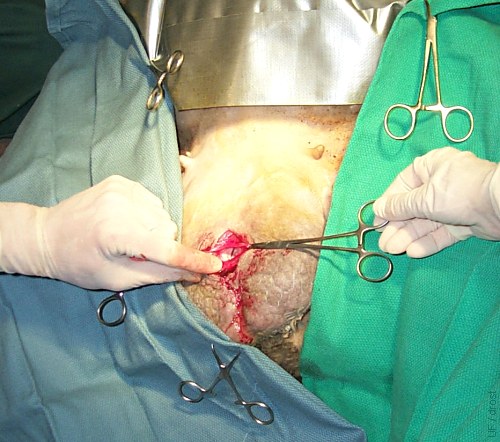
Location of Incision.
A cranial midscrotal approach for vasectomy uses a single midline skin incision. The tunic on each side is then incised and a section of vas deferens grasped and exteriorized.
Smith MC (2006)
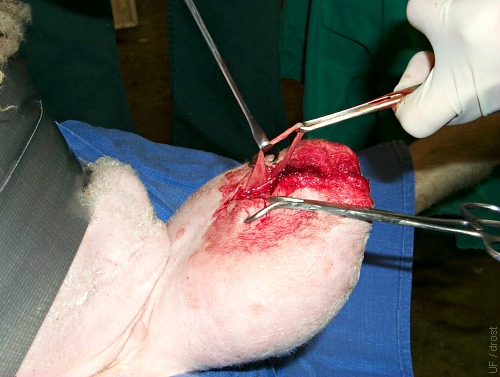
Isolated Vas Deferens.
Isolated vas deferens is ready for ligation and resection. Midscrotal approach.
Smith MC (2006)
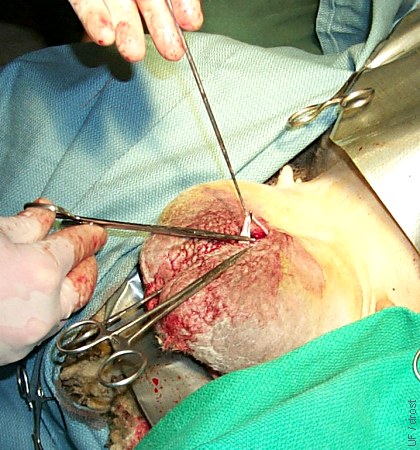
Ligating Close-up.
Grasping the ligated vas deferens in preparation for excising a segment.
Smith MC (2006)
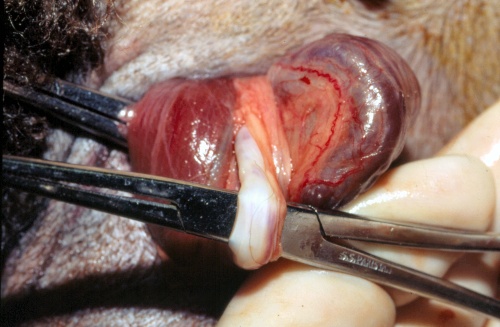
Vasectomy.
The cremaster muscle is on the left, the vas deferens is isolated with a pair of hemostats, and the pampiniform plexus is on the right, in this picture.
Pugh DG (2007)
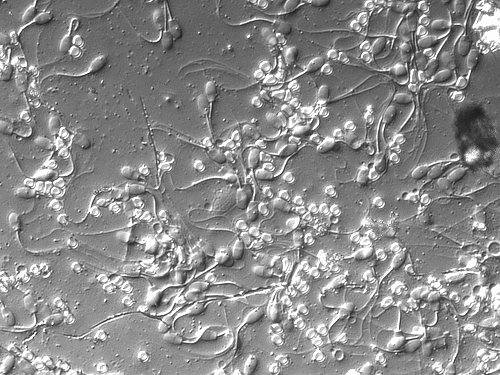
Vasectomy Smear.
Smear of the ejaculate after vasectomy. Numerous spermatozoa were still present in the distal portions of the vasa deferentia.
Smith MC (2010)
