The Visual Guide to
Ovine Reproduction
Male Reproductive System: Castration
Elastrator.
The young ram is suspended by the hind legs. The rubber band is placed on the elastrator.
Shipley C (2006)
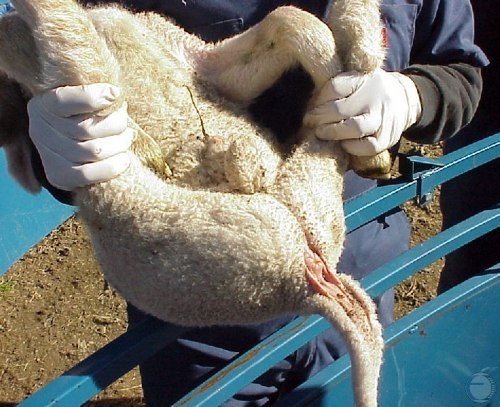
Positioning the Lamb.
Simple restraint of young lambs by grasping the front leg and the hindleg on each side with one hand respectively. This young lamb is now ready to be castrated.
Villarroel A (2013)
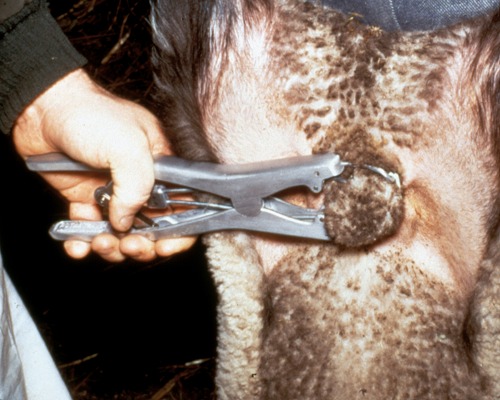
Elastrator Placement.
The elastrator band is placed around the neck of the scrotum and the spermatic cords to castrate this young ram.
Shipley C (2006)
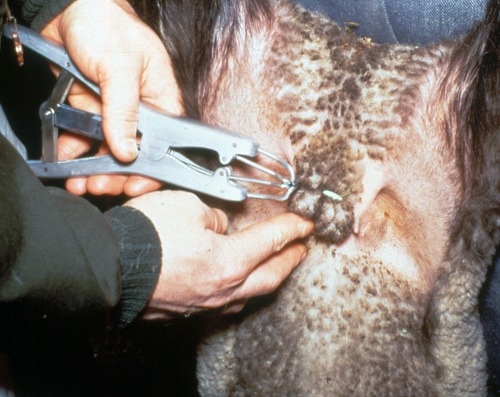
Elastrator Placement.
The elastrator band is tightened around the neck of the scrotum and the spermatic cords to castrate this young ram.
Shipley C (2006)
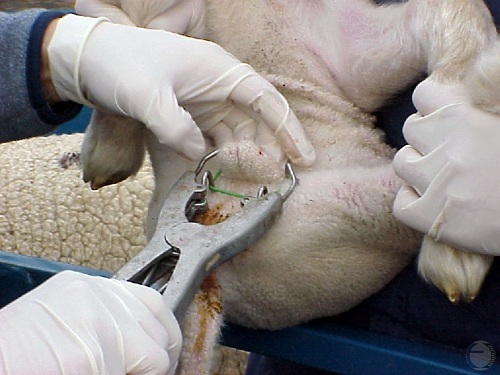
Placement.of the Elastrator.
The elastrator band is placed around the neck of the scrotum and the spermatic cords for castration of this young ram.
Villarroel A (2013)
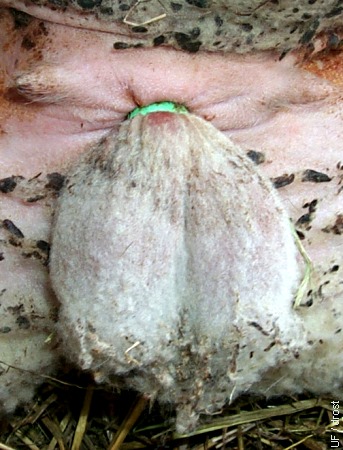
Banding > 1 Week.
One week after placement of the elastrator band around the neck of the scrotum.
Smith MC (2006)
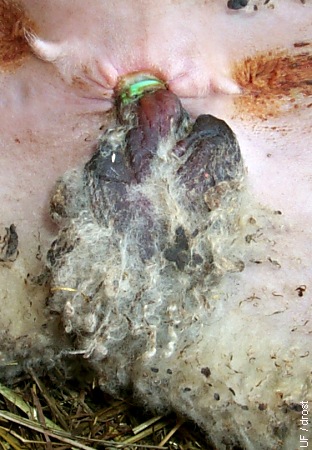
Banding > 2 Weeks.
Two weeks after placement of the elastrator band. Necrosis is evident.
Smith MC (2006)
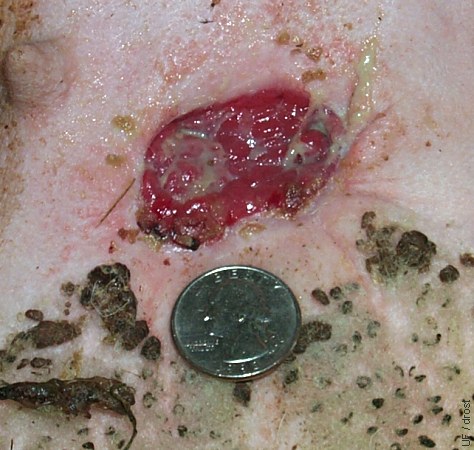
Banding > 4 Weeks.
Four weeks after placement of a Callicrate band on a mature ram. The scrotum and its contents have fallen off. The wound is granulating in. The length of the wound is ~30 mm (the diameter of the coin, a quarter, is 24 mm).
Smith MC (2006)
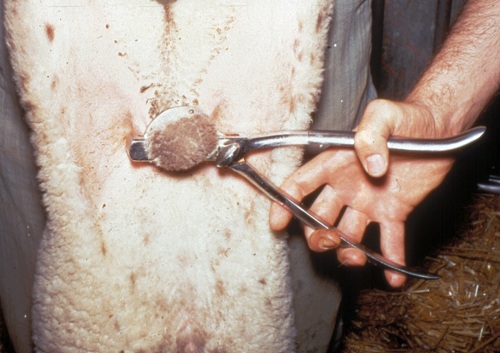
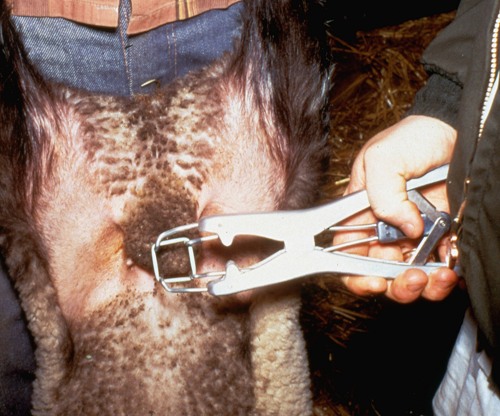
Emasculator.
Placement of an emasculator around the entire neck of the scrotum prior to crushing the spermatic cords and severing the scrotum and the testicles.
Shipley C (2006)
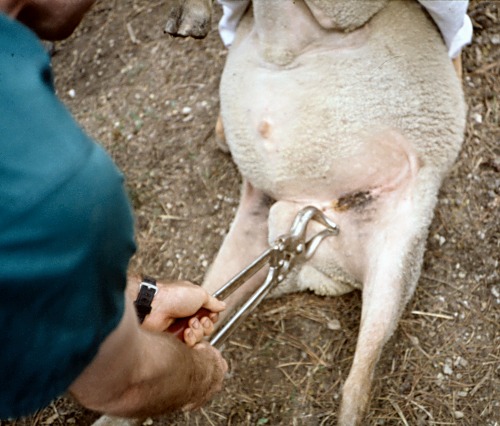
Burdizzo Castration.
The left spermatic cord is clamped, and functionally severed, with the Burdizzo instrument. One advantage of this bloodless procedure is subsequent absence of wound infection and fly problems.
Pugh DG (2007)

Emasculation with the Burdizzo.
The left leg of the ram has been pulled up and out of the way to provide better exposure for the camera. Each spermatic cord is clamped individually, to avoid disrupting the blood supply to the skin of the bottom of the scrotum, by leaving a strip of skin intact in the center of the scrotum.
Pugh DG (2007)
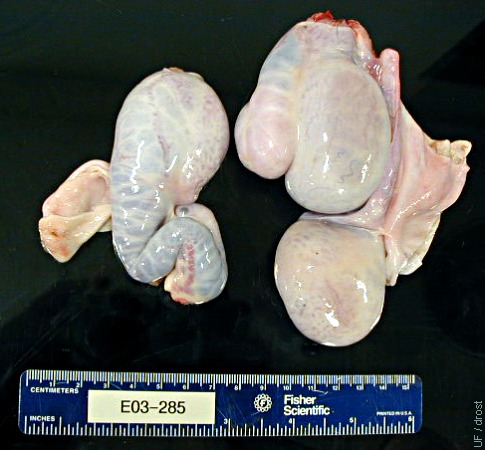
Burdizzo / Epididymis.
This animal was incompletely castrated with a Burdizzo. The testes have atrophied but the surviving epididymides are proportionately enlarged because their blood supply was not interrupted. The lower mass on the right is epididymis.
Smith MC (2006)
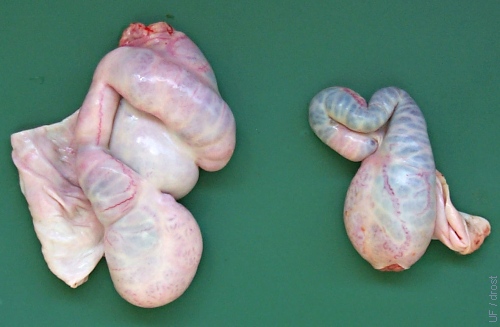
Burdizzo / Enlarged Epididymis.
Previous incomplete castration with a Burdizzo spared the blood supply to the epididymis bilaterally. The testis on the left is greatly atrophied while the other has virtually disappeared. The burdizzo was applied above the testes.
Smith MC (2006)
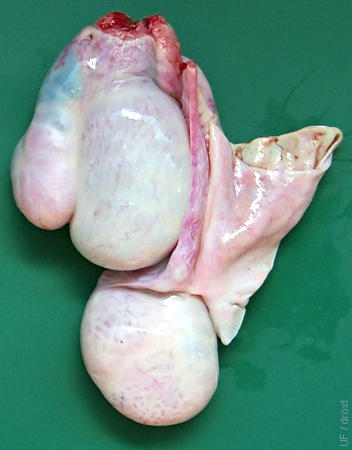
Burdizzo / Enlarged Vas.
The testis is atrophied but still present after incomplete Burdizzo castration. Visible are also the head (on left) and enlarged tail (below) of the surviving epididymis and the vas deferens with accompanying blood supply ascending on the right.
Smith MC (2006)
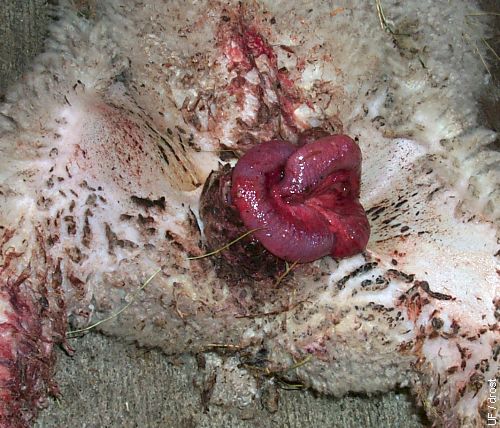
Eventration After Castration.
Prolapse of the intestines through the castration wound. This accident could have occurred because of too large an inguinal ring or stretching of the ring by excessive tension on the testes.
Smith MC (2006)
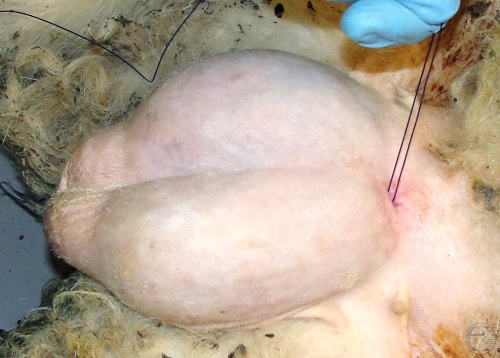
Pinhole Castration.
With the ram lamb in dorsal recumbency, the spermatic cord was pulled laterally and a 26 gauge needle was inserted in a caudal to cranial direction through the scrotal skin, adjacent to the medial aspect of the spermatic cord. Next # 1 chromic catgut was threaded through the needle. The hypodermic needle was then reinserted through the same holes, caudal to cranial, but this time lateral to the spermatic cord, and the suture material again threaded through the needle which was then withdrawn. The spermatic cord was ligated by tying the ends of the suture.
Villarroel A (2013)
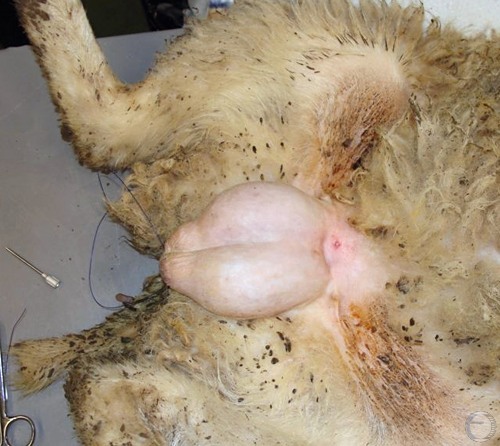
Pinhole Castration.
The cranial needle hole, following a "pinhole castration", is visible at the base of the spermatic cord dorsal to the testicle.
Villarroel A (2013)
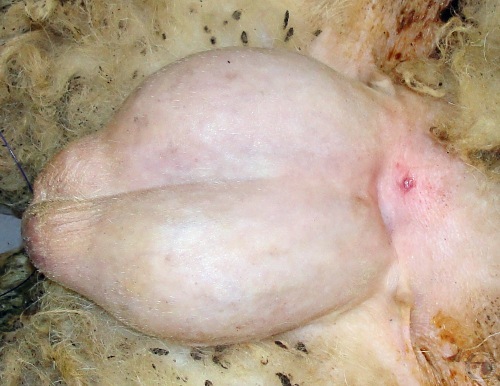
Pinhole Castration.
The cranial needle hole, following "pinhole castration", is visible at the base of the spermatic cord dorsal to the testicle.
Villarroel A (2013)
