The Visual Guide to
Porcine Reproduction
Male Reproductive System: Testis and Epididymis
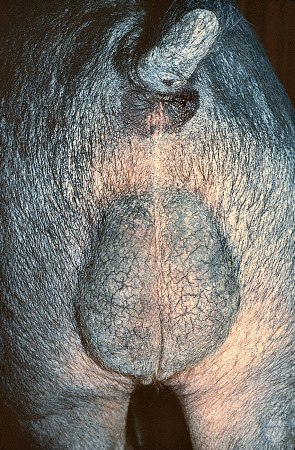
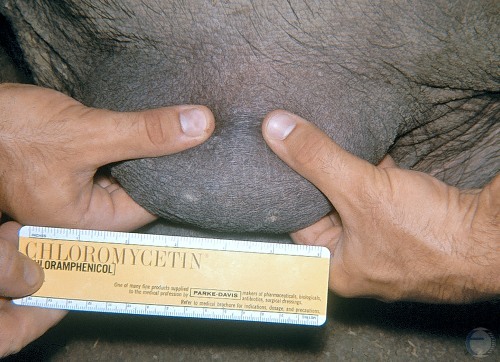
Normal Boar Testes.
Normal boar testes. They are examined for size, shape, symmetry, and consistency. In the adult boar they will measure 12 to 13 cm in length and 7 to 8 cm in width. In an eight month old boar the dimensions would be 9 by 6 cm, excluding the epididymis.
Evans LE (2009)
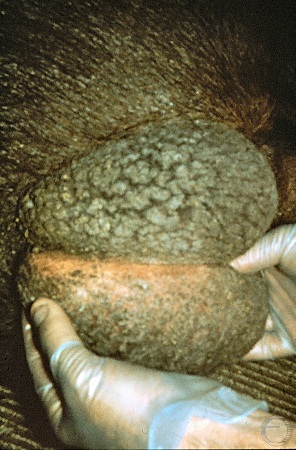
Normal Testis and Epididymis.
Normal testis and epididymis. The tail (cauda) of the epididymis is on the left. In the boar the tail of the epididymis is located caudal-dorsal in the scrotum with the body running along the lateral side of the testes and the vas deferens on the medial side.
Evans LE (2009)
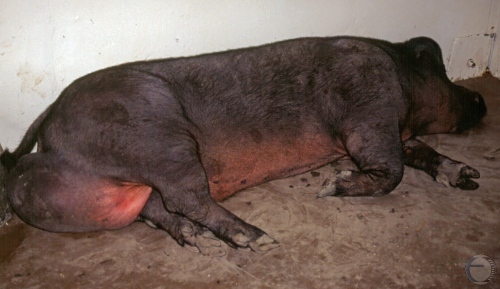
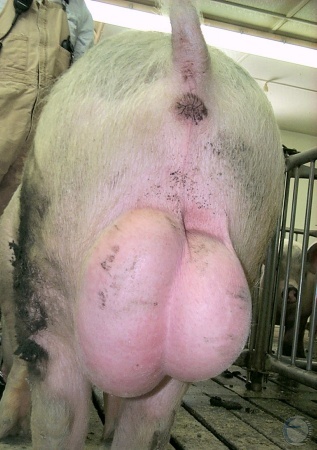
Testicular Hematoma.
Recumbent boar with a grossly enlarged scrotum as a result of a testicular hematoma.
Shipley C (2006)
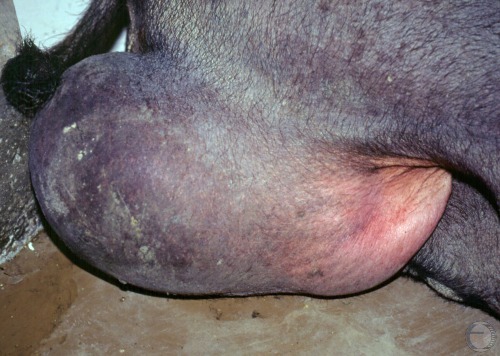
Testicular Hematoma.
Close up of the grossly enlarged scrotum of a boar, in left lateral recumbency, with a testicular hematoma.
Shipley C (2006)
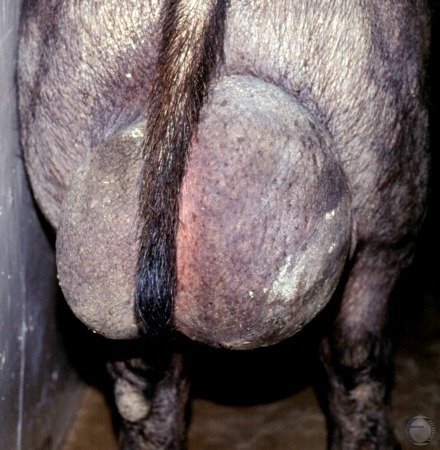
Testicular Hematoma.
Close up of the grossly enlarged scrotum of a boar with a hematoma of the right testis.
Shipley C (2006)
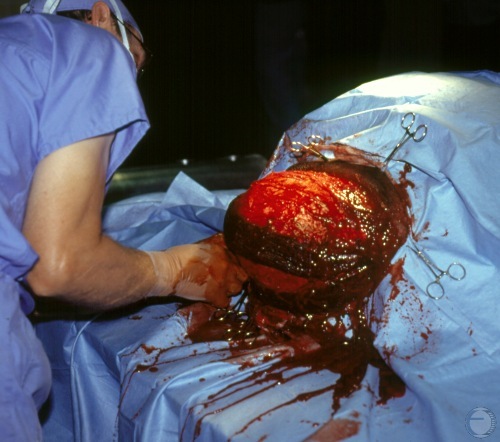
Testicular Hematoma.
Surgical exposure of large hematoma of the right testicle of a boar.
Shipley C (2006)
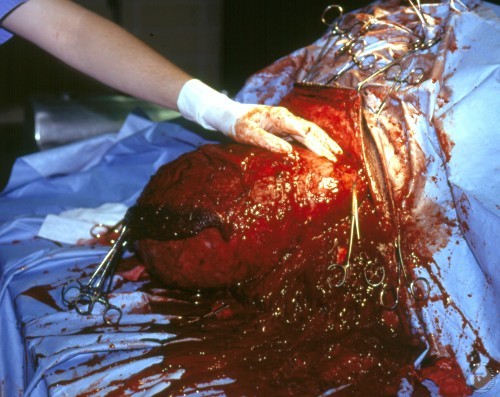
Testicular Hematoma.
Surgical exposure of large hematoma of the right testicle of a boar. [medium sized hand]
Shipley C (2006)
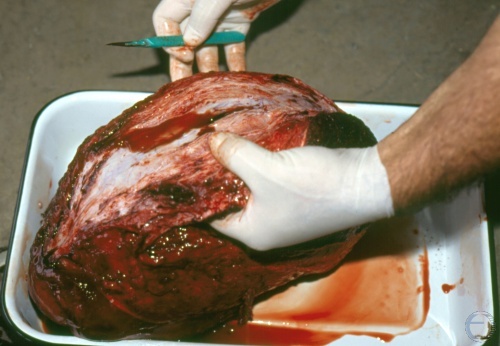
Testicular Hematoma.
The fingers of the right hand are inserted in the empty cavity of the testicle. [length of the green scalpel is 13 cm]
Shipley C (2006)
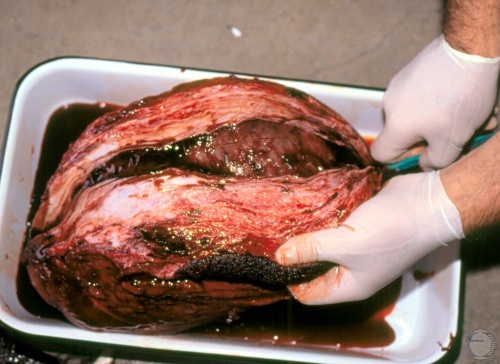
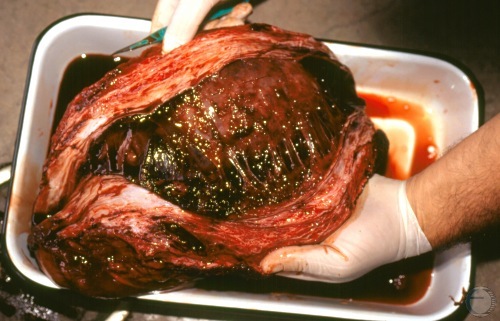
Testicular Hematoma.
Incision of the hematoma to expose the cavity. The scrotal skin has been removed. Cross section of the testis showing the cavity of the collapsed hematoma.
Shipley C (2006)
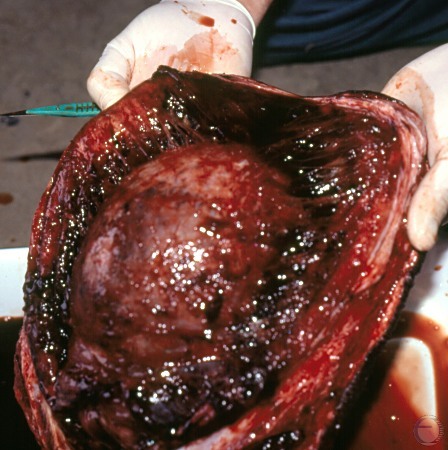
Testicular Hematoma.
Cavity of the hematoma opened up. Testis intact.
Shipley C (2006)
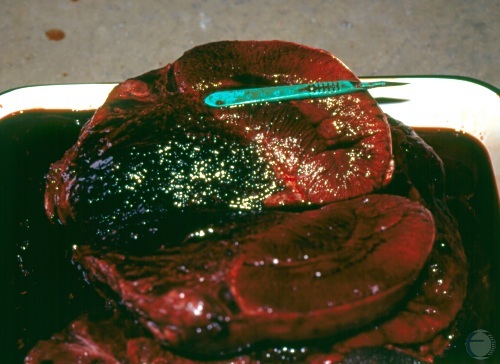
Testicular Hematoma.
Cross section of the testis. Presence of a large blood clot. [length of the green scalpel is 13 cm]
Shipley C (2006)
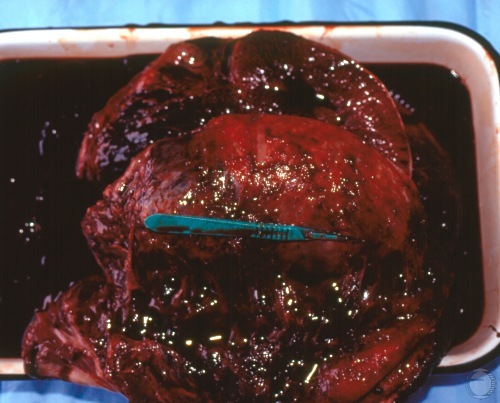
Testicular Hematoma.
Intact testis surrounded by clotted blood. [length of the green scalpel is 13 cm]
Shipley C (2006)
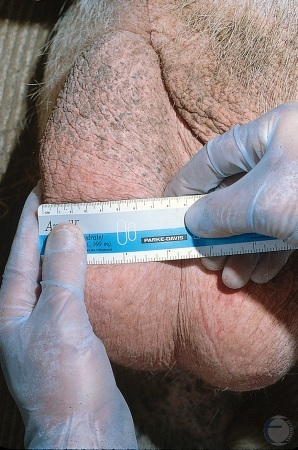
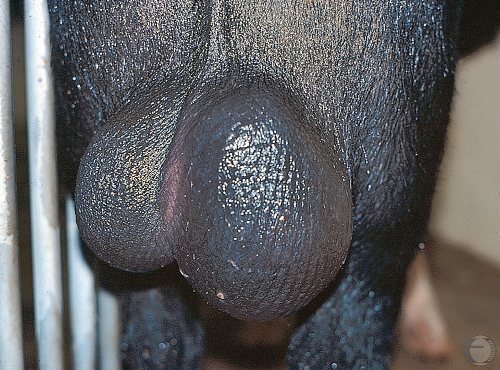
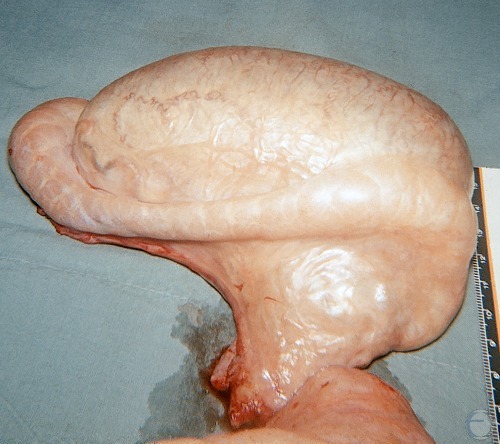
Testicular Measurements.
Measurements of the testicles of a normal adult boar are 6 to 7 cm wide and 10 to 12 cm long. Epididymal tissue is not included in the measurements.
Evans LE (2009)
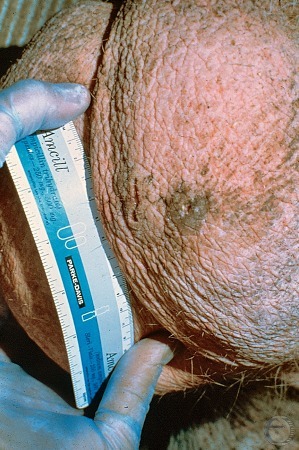
Testicular Measurements.
Measurements of the testicles of an adult boar: 10 to 12 cm long, 6 to 7 cm wide. Epididymal tissue is not included in the measurement. The tail of the epididymis is located at the top of (dorsal to) the testicle.
Evans LE (2009)
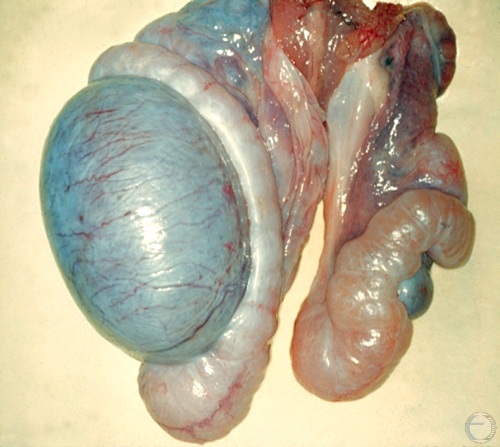
Testicular Hypoplasia.
The testicle on the right is hypoplastic and barely recognizable. The accompanying epididymis is distended. The contralateral testis and epididymis are normal.
McEntee K (1973)

Unilateral Testicular Hypoplasia.
Unilateral testicular hypoplasia. The right testicle is smaller than normal.
Evans LE (2009)
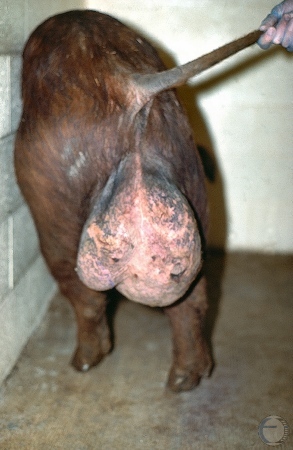
Funiculitis.
Unilateral orchitis. Inflammation of the right spermatic cord (funiculus) and tunics around the testicle.
Evans LE (2009)
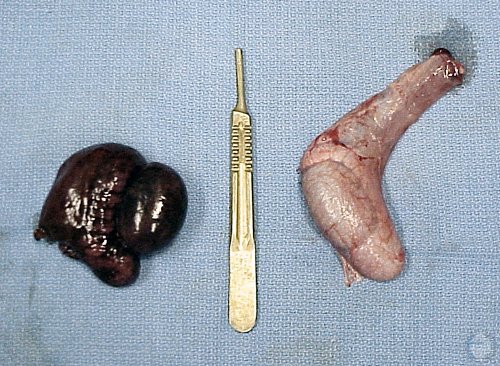
Cryptorchid and Testicular Torsion.
Left testicle congested with clotted blood due to strangulation of the spermatic cord. Right testicle is normal. [length of the scalpel handle = 13 cm].
Shipley C (2006)
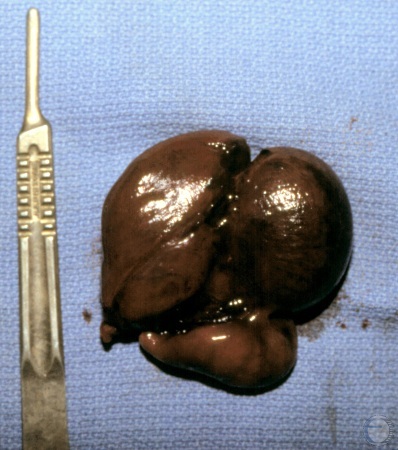
Cryptorchid and Testicular Torsion.
Left testicle and epididymis congested with clotted blood due to strangulation of the spermatic cord. [length of the scalpel handle = 13 cm].
Shipley C (2006)
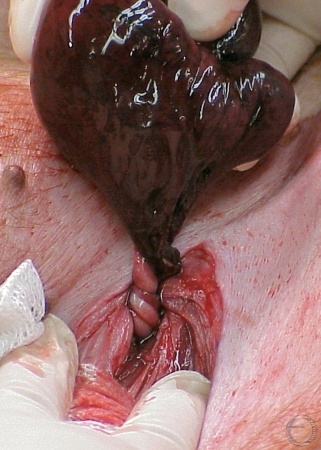
Cryptorchid and Testicular Torsion.
Twisted spermatic cord and occlusion of the blood supply.
Shipley C (2006)
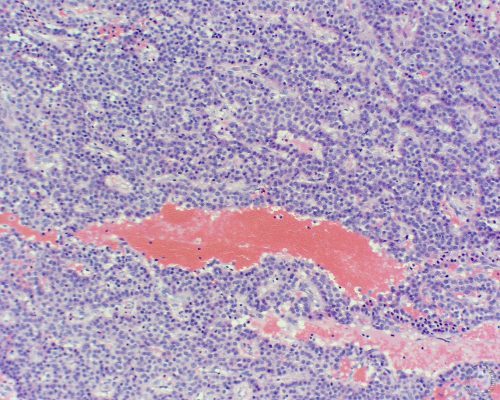
Interstitial Cell Tumor.
Histology of an interstitial tumor in a boar.
Smith MC (2011)
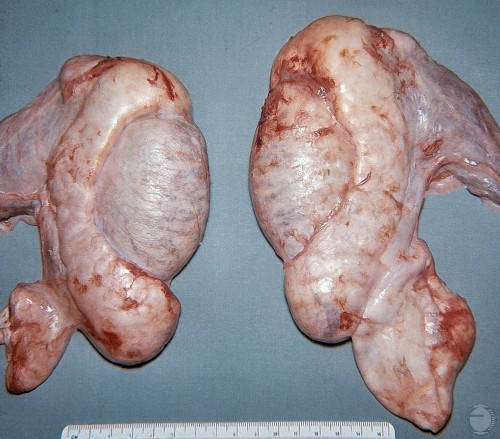
Bilateral Testicular Atrophy.
The atrophic testicles are flaccid and small (length 7 to 8 cm, width 4 cm). Note the disproportion between the epididymides and the testes.
Evans LE (2009)
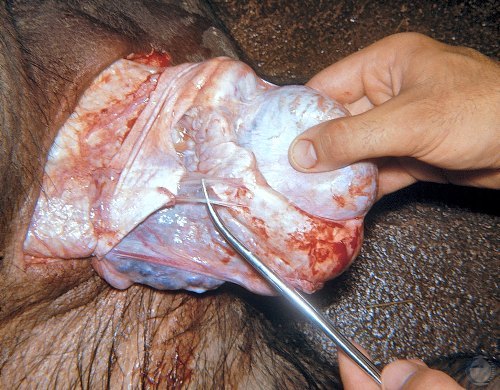
Testicular Atrophy with Scrotal Adhesions.
The flaccid, atrophic testis and epididymis are adhered to the wall of the scrotum.
Evans LE (2009)
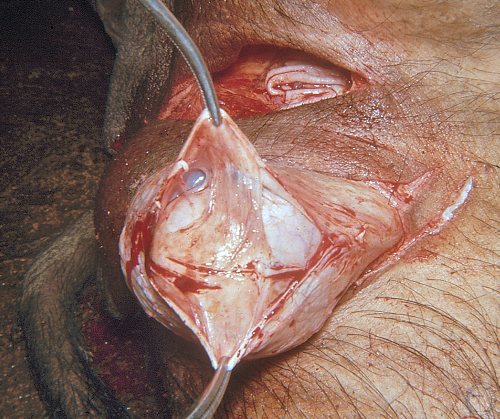
Testicular Atrophy with Scrotal Adhesions.
The flaccid, atrophic testis and epididymis are adhered to the wall of the scrotum.
Evans LE (2009)
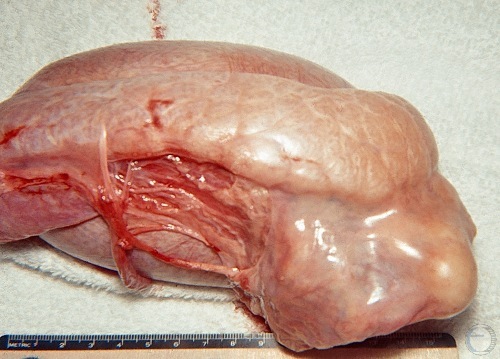
Testicle from Aspermic Boar.
Testicle from an aspermic boar. Note the sperm granuloma (right ventral area) due to aplasia of the rete testis and ductal occlusion. The condition was bilateral.
Evans LE (2009)
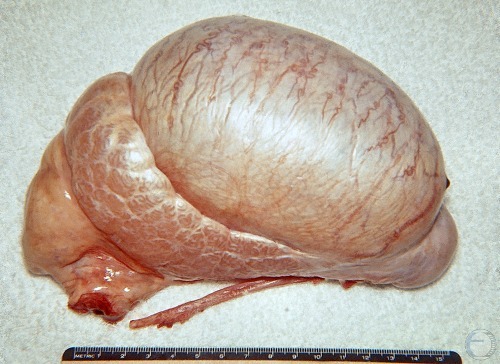
Sperm Granuloma.
Normal size testicle from an aspermic boar. Bilateral sperm granuloma at the head of the epididymis (right side of image) and segmental aplasia in the rete testis.
Evans LE (2009)
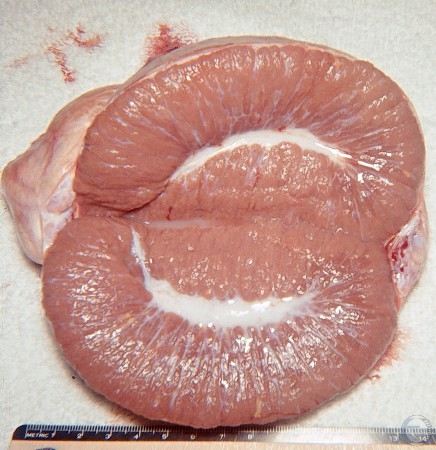
Semen in Mediastinum of Aspermic Boar.
Normal sized testis from an aspermic boar. Bilateral sperm granuloma at the head of the epididymis (right side of image) and segmental aplasia in the rete testis. Sperm is present in the mediastinum testis.
Evans LE (2009)
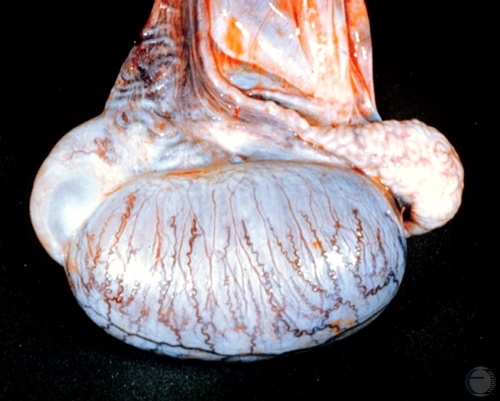

Vestigial Cyst.
Vestigial cyst on the head of the epididymis (smooth fluctuant area on the left).
McEntee K (1973)
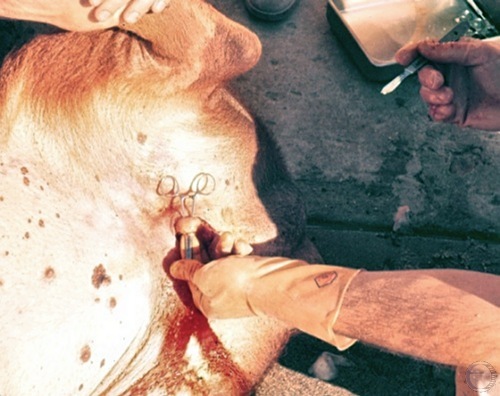
Vasectomy 1.
The boar is in dorsal recumbency and an incision was made anterio-ventral to the scrotum. Next the spermatic cord was palpated and exposed with the aid of a pair of forceps.
Roberts SJ (1973)
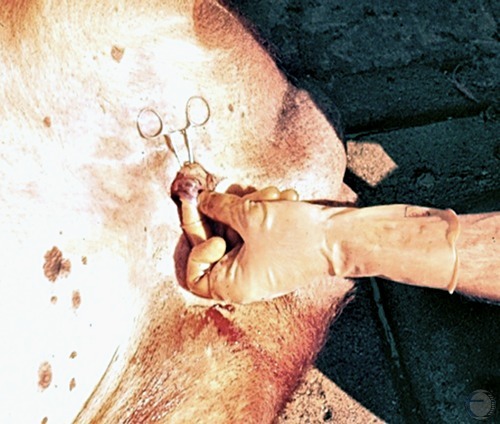
Vasectomy 2.
Exposure of the spermatic cord, showing the pampiniform plexus.
Roberts SJ (1973)
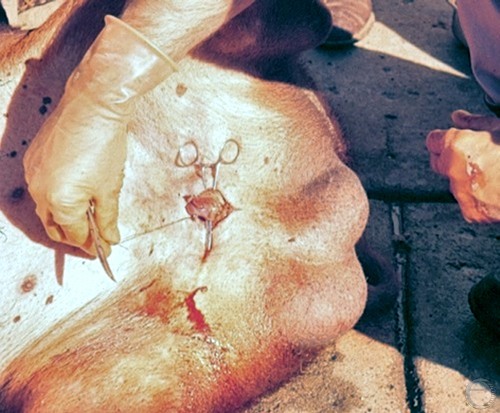
Vasectomy 3.
Ligation of the vas deferens. It is recommended that the cord be double ligated to prevent leakage of semen and possible formation of a spermatocele.
Roberts SJ (1973)
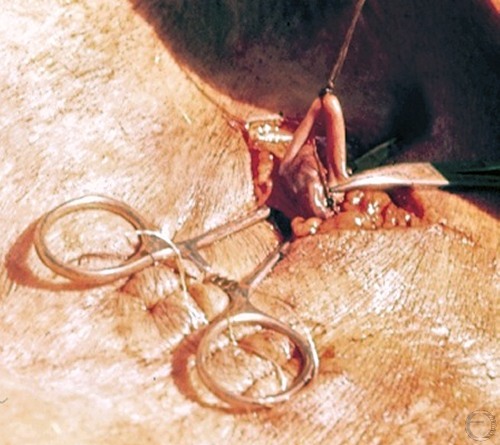
Vasectomy 4.
Transection of the vas deferens with scissors (tip on the right). It is recommended that the cord be double ligated to prevent leakage of semen and possible formation of a spermatocele.
Roberts SJ (1973)
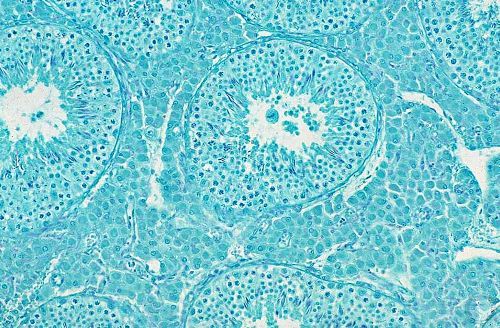
Histology of the Testis.
Histological section of a normal testis in full production. Note elongated spermatozoa in the lumen.
Evans LE (2009)
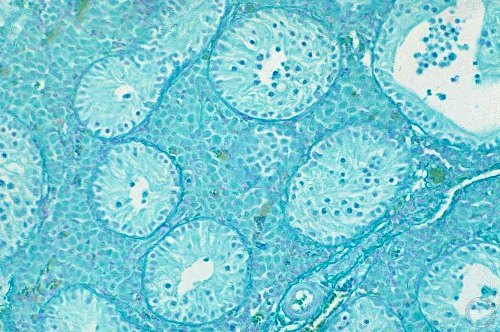
Histology of the Testis.
Histology of the testis after spermatogenic arrest. There are spheroids in the lumen but no sperm cells.
Evans LE (2009)
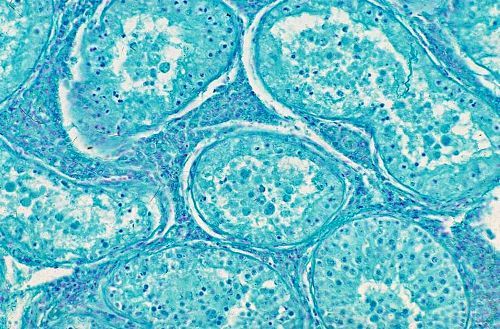
Histology of the Testis.
Histology of the testis after spermatogenic arrest. There are spheroids in the lumen. Some of the spheroids are multi nucleated.
Evans LE (2009)