The Visual Guide to
Canine Reproduction
- Testis and Epididymis
- Scrotum
- Accessory Sex Glands
- Penis
- Prepuce
- Semen
- Breeding Soundness Evaluation
- Castration
Male Reproductive System: Testis and Epididymis
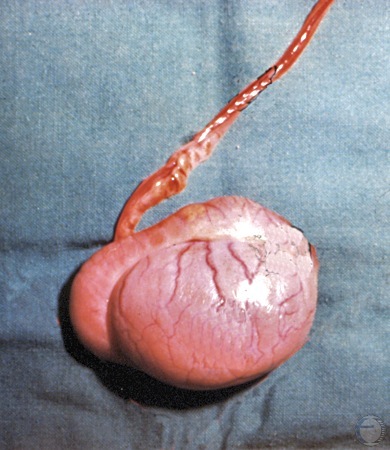
Normal Testis.
Normal healthy adult testis, epididymis and vas deferens.
Shille VM (1977)
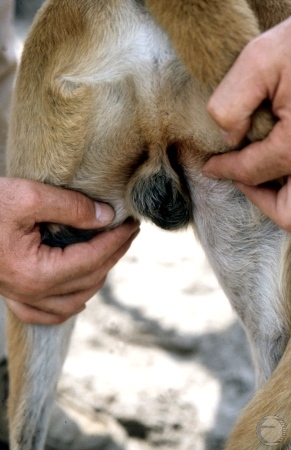
Examination of the Testis.
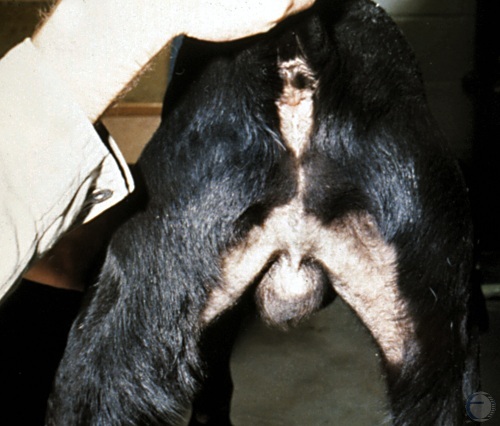
Visual examination of the testes. The normal scrotum should fill the space between the upper thighs. One testis is usually suspended slightly higher than the other.
Shille VM (1982)
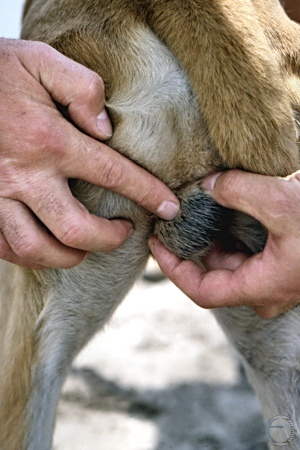
Palpation of the Epididymis.
The index finger of the hand on the left identifies the epididymal border.
Shille VM (1982)
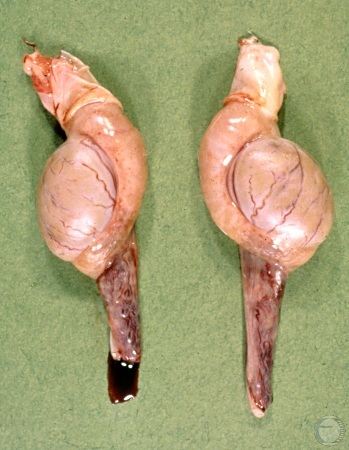
Epididymitis.
Bilateral epididymitis. Note the disproportion between the epidimymides and the testes. Etiology unknown.
Shille VM (1982)
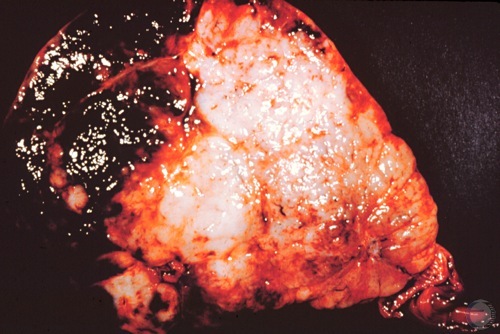
Seminoma.
Seminomas are generally gray in color, semi-firm in texture, and they are unilateral. Hemorrhage due to biopsy.
McEntee K (1972)
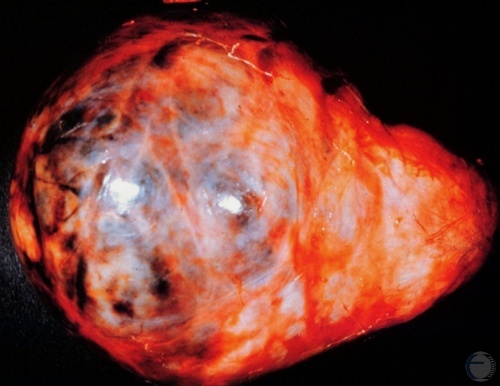
Seminoma.
Seminomas can become quite large and can occur in undescended testes (in 20% of the cases).
McEntee K (1972)
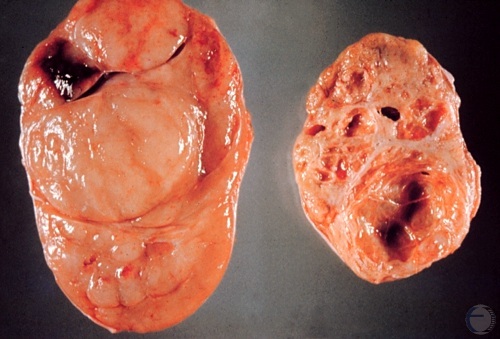
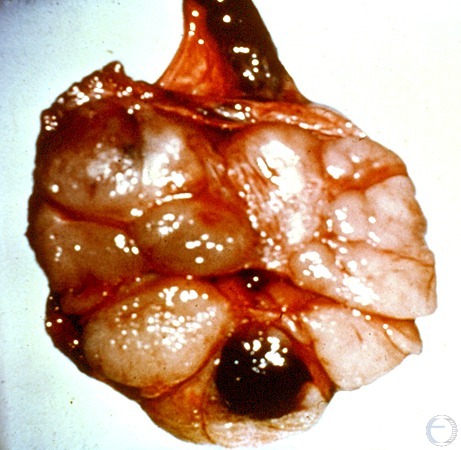
Seminoma - Cross-section.
Seminoma. Parenchymal tissue almost entirely replaced by bulging multilobulated tumor tissue.
McEntee K (1972)

Interstitial Cell Tumor.
This testicular cell tumor or Leydig cell tumor is a benign tumor. The tumor mass per se is discrete and soft.
McEntee K (1972)
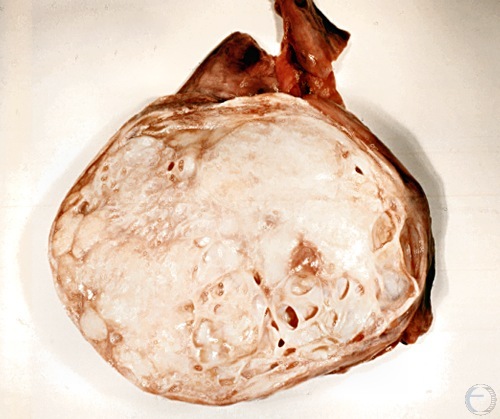
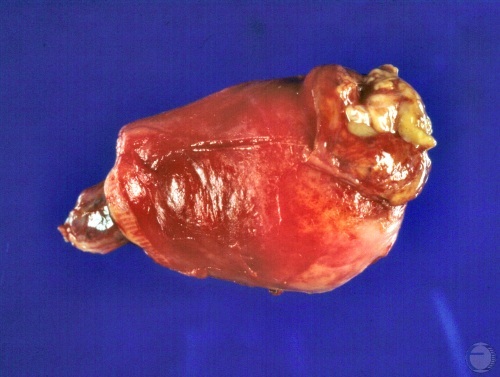
Sertoli Cell Tumor.
Sertoli cell tumor also called sustentacular cell tumor. The entire parenchyma has been replaced by white tumor tissue with occasional cysts. The testis is enlarged.
Roberts SJ (1973)
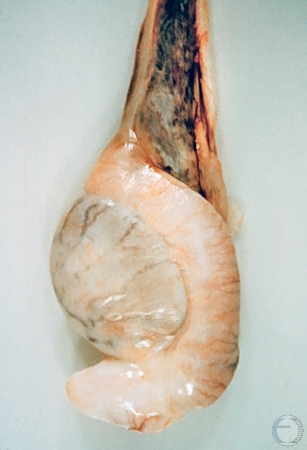
Testicular Degeneration.
Notice the disproportion between the testicular parenchyma and the epididymis. The consistency of the testis is soft. The delineation between the testis and the epididymis is readily apparent.
McEntee K (1972)
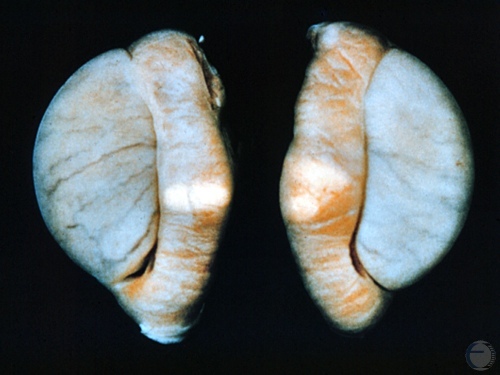
Sperm Granuloma.
The testes feel normal. The epididymides are slightly enlarged and feel firm and lumpy. When this occurs bilaterally the dog is azoospermic.
McEntee K (1972)
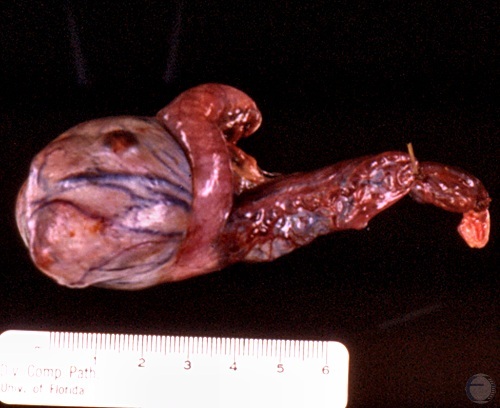
Testicular Granuloma.
Testicular granuloma. Notice two bulging nodules.
Shille VM (1986)
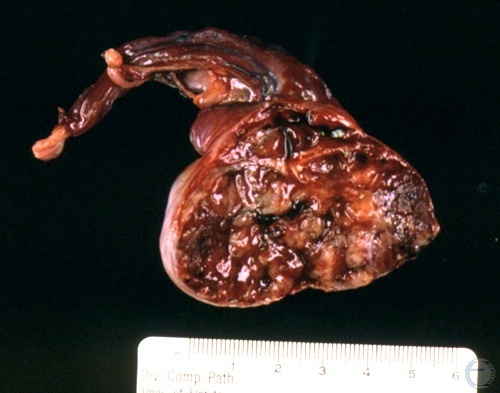
Granuloma Cross-section.
Cross section of a testicular granuloma.
Shille VM (1986)
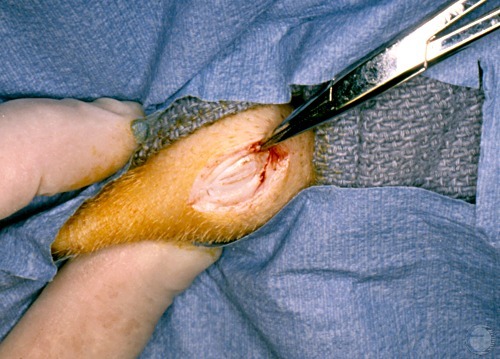
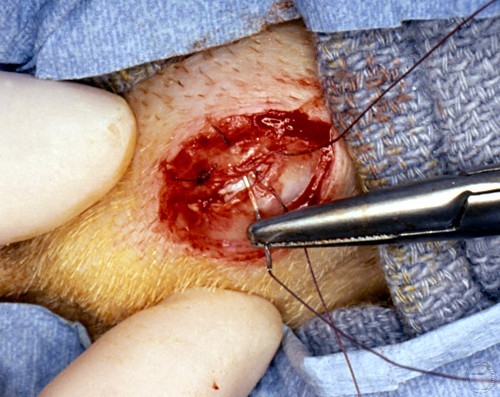
Testicular Biopsy.
After surgical preparation a careful skin incision is made while hemorrhage is controlled with a hemostat.
Shille VM (1980)
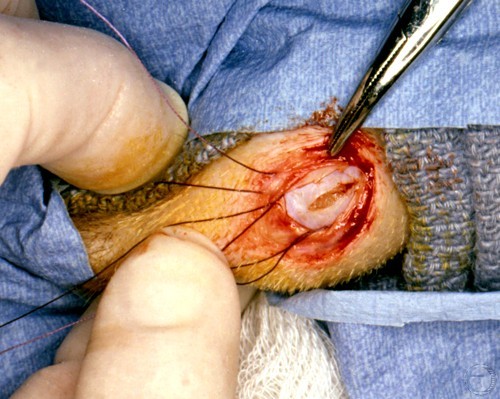
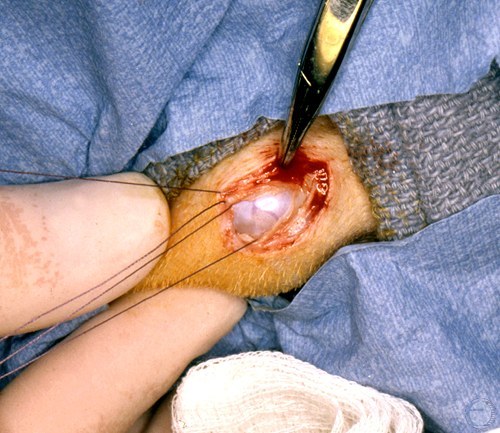
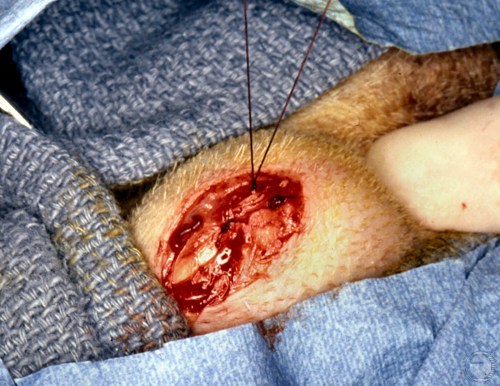
Testicular Biopsy.
Incision through the tunics into the testicular parenchyma and that is sampled.
Shille VM (1980)
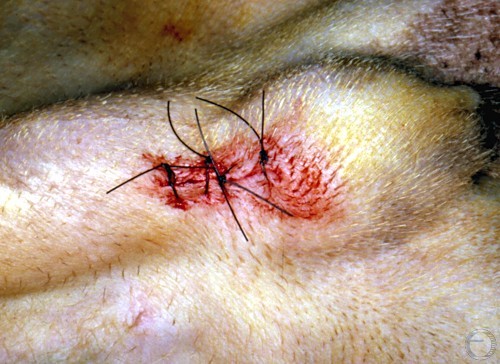
Testicular Biopsy.
Prescrotal skin closure complete after testicular biopsy procedure.
Shille VM (1980)
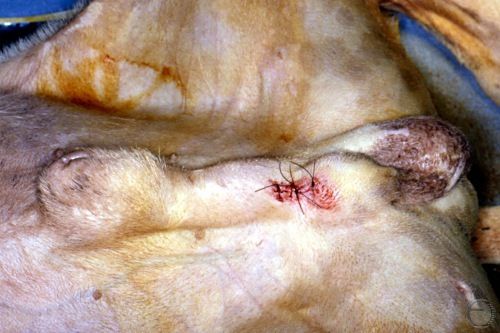
Testicular Biopsy.
Biopsy procedure completed. Note location of the skin incision.
Shille VM (1980)
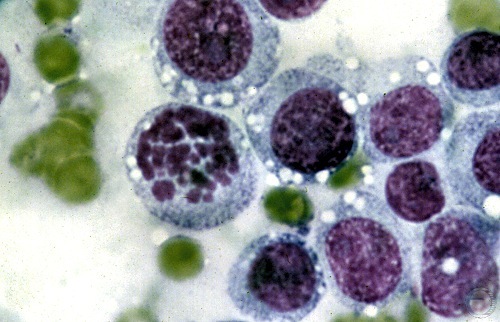
Transmissible Venereal Tumor Cytology.
Large round cells, resembling lymphocytes, typical of transmissible venereal cell tumor. Nuclei are round, vesicular, and eccentric.
Shille VM (1980)
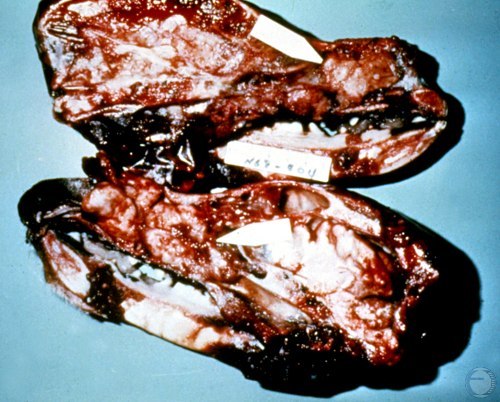
Nasal Transmissible Venereal Tumor.
Sagital section of the skull. Transmission of a venereal tumor to the nose.
Shille VM (1980)
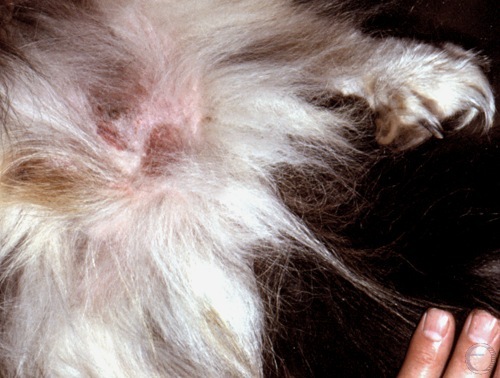
Inguinal Hernia.
The enlarged inguinal ring and the hernial sac can be palpated.
Shille VM (1980)
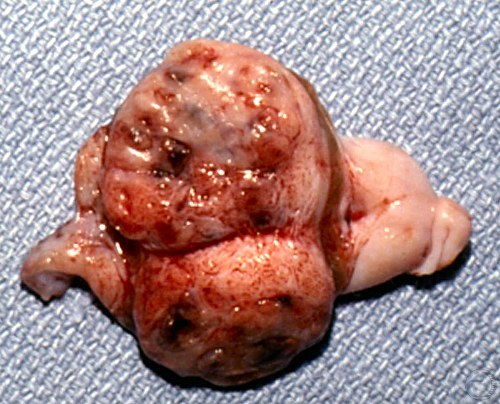
Retained Testis.
Cross-section of a retained testicle showing neoplasticparenchyma.
Shille VM (1980)
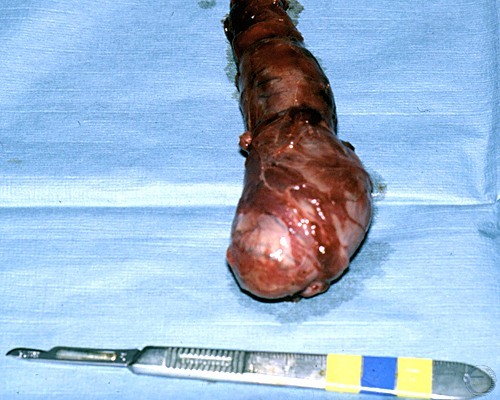
Infarcted Testis.
Sudden insufficiency of the blood supply to the testis (infarction).
Shille VM (1980)
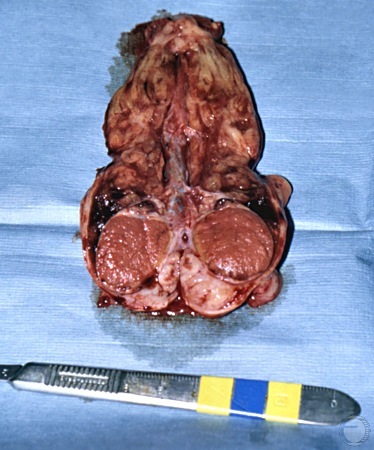
Infarcted Testis - Cross-section.
Despite major infarction of the testicular cord the testis appears grossly normal.
Shille VM (1980)